What Are Immunoglobulins?
Immunoglobulins are a special group of molecules that we find within the protein family. The main function of this class of biomolecules is protective, that is, they serve to protect the organism.
This situation usually occurs before the invasion of other living beings that are recognized as strangers within us. For example, this is the case of viruses, bacteria, cells that are not their own, such as those from a transplant, etc. That is, they are important for the immune system to function properly.
Why are we synthesized immunoglobulins?
Immunoglobulins are also called antibodies and their synthesis depends on specialized cells that are part of the immune system. Their formation increases if antigens are identified or perceived. These are foreign substances present in foreign agents like bacteria, viruses, etc. Thanks to the corresponding studies, it has been possible to verify that this plasma protein is synthesized by B lymphocytes and by certain plasma cells.
Also, the immune system is very precise, producing different antibodies or immunoglobulins for each antigen. This characteristic ensures our survival, but shows failures such as autoimmune diseases.
In patients with these types of alterations, immunoglobulins recognize the patient’s own cells as “foreign”. For this reason, they intend to neutralize this apparent threat by destroying those healthy cells as if it were a pathogen.
On the other hand, immunoglobulins or antibodies normally use the bloodstream to travel to another region of the body. In this way, they can quickly travel to the place where the antigens have been located and destroy them.
Because of this, the healthcare team usually carries out the study of blood samples to control the level of immunoglobulins. However, on other occasions you can take other fluid samples. For example, from saliva or other substances such as cerebrospinal fluid.
What types of immunoglobulins are there?
According to their characteristics and functions, we can distinguish between various types of immunoglobulins or antibodies.
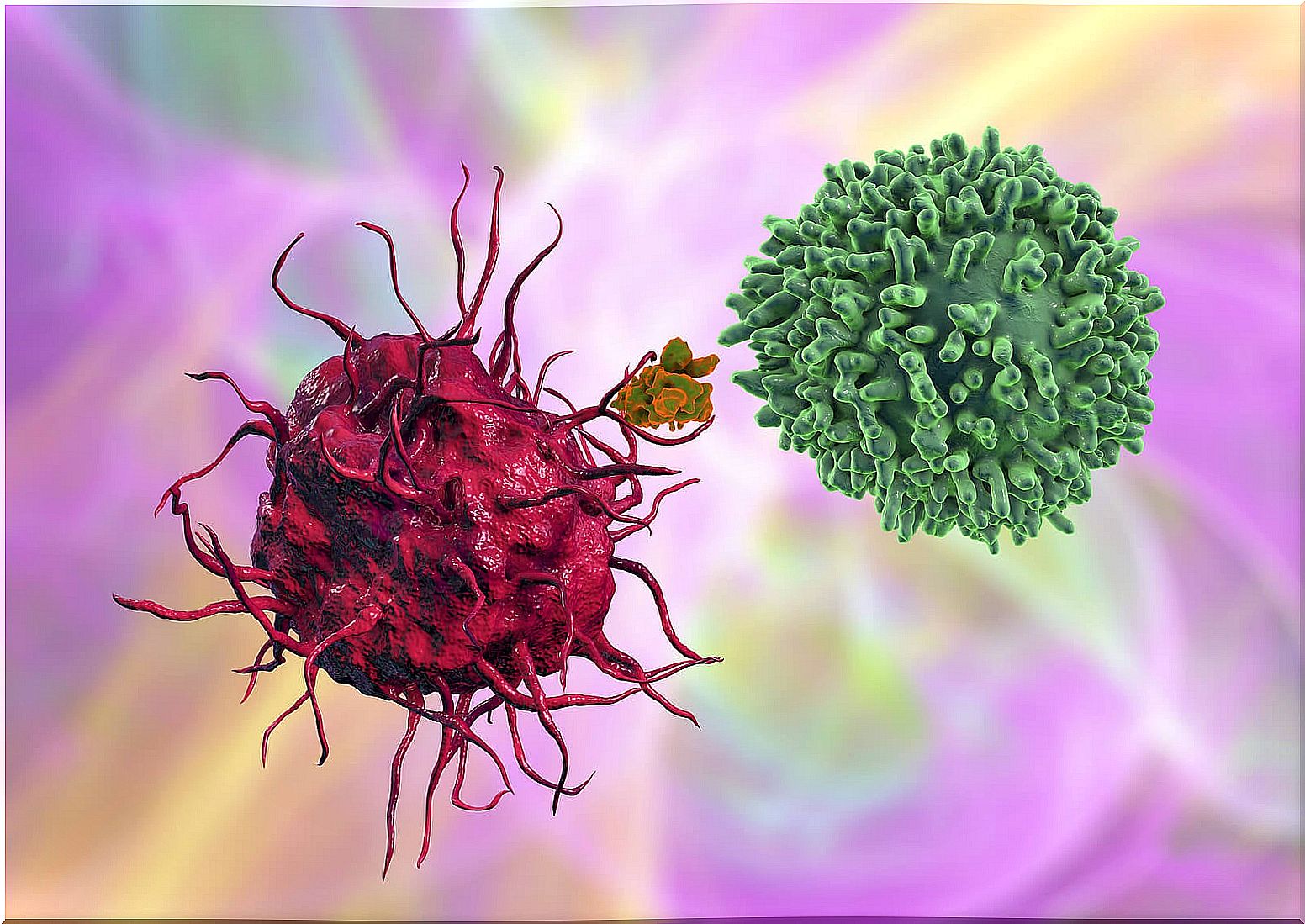
Immunoglobulins G or Ig G
It is the most numerous type of immunoglobulin. It can be said that they are innate and confer immunity on babies from birth. This fact is due to the fact that they are present in the mother’s placenta. Thus, these antibodies are transferred from the mother to the developing baby.
In principle, people can be found in the body throughout life. They are involved in certain essential tasks such as the activation of phagocytes, that is, they destroy cells or remains by “ingesting” them.
Immunoglobulins M or Ig M
These molecules can form a circle-like structure that has up to ten binding sites (with antigens). As a general rule, they make the “first contact” with newly identified antigens. They activate or promote the action of macrophages (similar to phagocytes).
Immunoglobulins A or Ig A
These have a heavy chain of the alpha type. We find them in the form of monomers, dimers or trimers. This means that up to three units or immunoglobulins may appear attached.
In addition, they are located in all body secretions that have a defense function. For example, in breast milk, blood, mucus, tears …
Immunoglobulins E or Ig E
This class of antibodies have an epsilon-type heavy chain. Unlike the aforementioned antibodies, they are usually placed on the mast cell membrane. Therefore, the majority of these types of immunoglobulins reside in body tissues.
Normally they are the receptors of allergens, antigens that provoke a very exaggerated response. They are not dangerous substances per se, but the immune system recognizes them as a serious threat. They cause the breakdown of the mast cell and the massive release of histamine into the body.
Immunoglobulin D or Ig D
These antibodies are made up of heavy chains of the delta type. They can be identified in the membrane of B lymphocytes.
To consider
In summary, “immunoglobulins are glycoproteins that, as Porter indicated in 1959, they are formed by polypeptide chains grouped, depending on the type of immunoglobulin, in one or more basic structural units ”.
While immunoglobulins (Ig) do not prevent all infections, they do reduce the frequency and severity of many infections in patients with PIDs. They also provide information on the immune system and therefore, the health status of people.