Diagnosis In Tennis Elbow
Tennis elbow, or epicondylitis, is a pathology characterized by pain in this joint due to prolonged repetition of movements and overexertion of the muscles. We tell you how is the diagnosis of this condition.
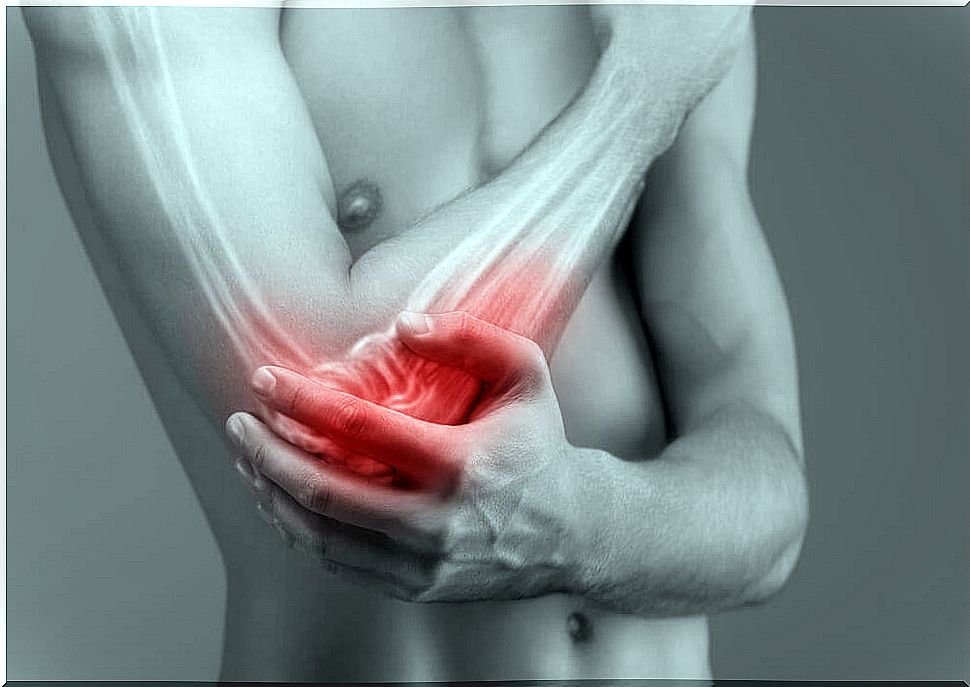
Epicondylitis, commonly known as tennis elbow, is the inflammation of the epicondylar tendons, which are ligaments that join the muscles of the forearm and hand with the humerus. These can become inflamed due to microtrauma from muscle strain.
This condition is very common within the sports field, hence its name, but there are also professions with a tendency to develop this injury, due to the repetition of specific gestures. This is the case of jobs where you must load weight or spend several hours at the computer. In the same way, in those of carpentry or any activity that implies an overexertion of the muscles in charge of the movements of the hand. Next, we tell you more about it.
Tennis elbow symptoms
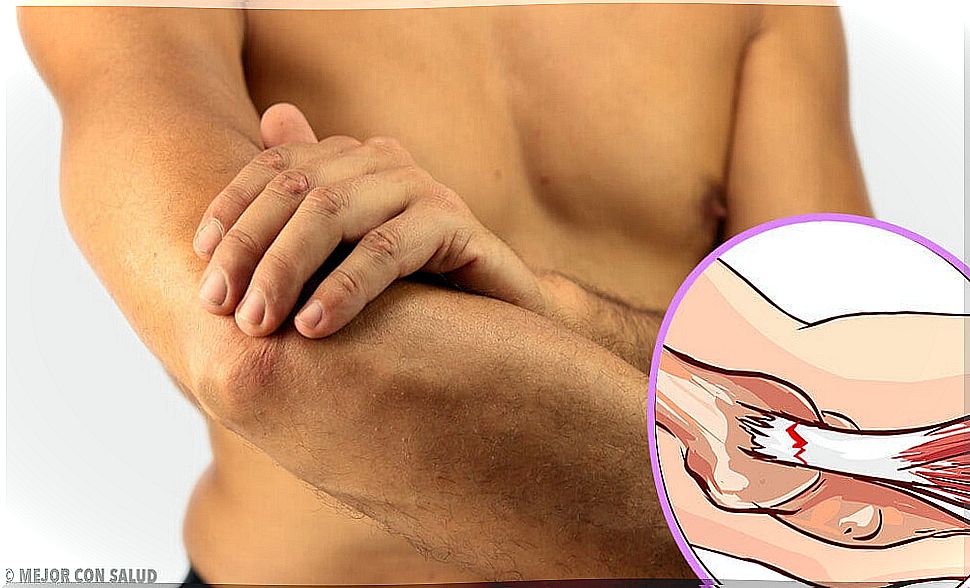
The symptoms of epicondylitis appear progressively and, in general, some pain is usually noticed on the outside of the elbow, which extends to the forearm. Also, according to a publication by the American Academy of Orthopedic Surgeons , there may be a lack of strength in the area and discomfort when grasping and holding objects, turning a key, or shaking hands.
Tennis elbow diagnosis
It is very important to make a correct differential diagnosis of the cause of elbow pain in order to carry out an adequate treatment, since there are different pathologies that have similar symptoms. Typically, the doctor checks that the pain appears at certain times, such as when palpating the side of the elbow or stretching the fingers.
In addition to this, a publication from the Radiological Society of North America suggests that, for a correct diagnosis of this degenerative process, the following protocol must be followed:
1. Patient’s medical history

The first thing the doctor will do is gather information about the patient’s daily activities that may have an influence on the pathology. In addition, they will perform a thorough examination of the physical appearance of the affected area to look for signs of inflammation, changes in the skin, deviation of the alignment of the joint, and so on. To do this, he will examine the epicondyle and proceed to palpate it, to check if the patient feels pain in that specific area.
Also, if he considers it necessary, he will perform the forced varus test. This consists of exerting an applied force on the elbow, which causes the distal face of it to move towards the midline of the body. The test will be positive if the patient reports discomfort. Next, an examination of the mobility of the elbow and head of the radius, cervical spine, and the entire joint complex of the shoulder will be done.
2. Other tests
If, with the previous examination, it cannot be determined that the cause of the pain is due to epicondylitis, the following complementary tests will be carried out:
- Analytical, to rule out the existence of uric acid crystals in the joint caused by hyperuricemia.
- Electromyography, to rule out nerve compression syndromes.
- Radiology and complementary tests.
Treatment
Tennis elbow usually gets better on its own. However, there are cases in which it is necessary to resort to other actions, in addition to the different self-care measures. In relation to this, a publication from the Mayo Clinic points out that physical therapy is a good option to learn to stretch and strengthen muscles. On the other hand, if it is a more serious case, it will be necessary to resort to the following procedures:
- Injections of plasma, botox, or some other irritant into the tendon.
- Ultrasonic tenotomy. This is done by inserting a needle into the affected part of the tendon to remove the damaged tissue.
- Surgery.
How to prevent tennis elbow?
One of the best ways to prevent the appearance of epicondylitis is to perform movements consciously so as not to strain the elbow muscles too much. In addition, it is important to avoid certain activities that imply an overexertion in the area. Also, do the proper stretching and, if necessary, use elastic elbow pads.