Thyroid Biopsy: Everything You Need To Know
Thyroid biopsy is a very common procedure today. It allows to extract samples from the gland and analyze them in the laboratory. This can diagnose or rule out many diseases, such as cancer.
There are different methods to perform the biopsy. The most used is by fine needle aspiration, although there are others that help when a clear diagnosis has not been achieved.
Thanks to the thyroid biopsy, a specific treatment can be established depending on the pathology. Therefore, in this article we explain everything you need to know about this exam, how it is performed and what it is for.
What is a thyroid biopsy?
The thyroid biopsy is a procedure used to diagnose different pathologies that affect this gland. The thyroid is an organ found in the front part of the neck, in front of the windpipe. It is responsible for producing hormones that have a fundamental role in controlling metabolism.
A thyroid biopsy consists of removing a sample of the tissue from the thyroid gland. This sample is examined in the laboratory, looking at it under a microscope.
As we have pointed out in the introduction, there are different ways to do it. The most common is fine needle aspiration biopsy. In these cases, it is usually done on an outpatient basis and using only local anesthesia.
However, other techniques do require general anesthesia and are somewhat more complex. The idea is to obtain part of the tissue from nodules that have appeared. In general, samples are taken from those that can be felt through the skin.
As stated in a RadiologyInfo publication , the nodules from which the sample is obtained are usually somewhat larger than 1 centimeter. In order to perform this test more safely or specifically, an ultrasound is performed simultaneously. Thanks to it, it is easier to locate the exact position of the nodules, especially if they are small.
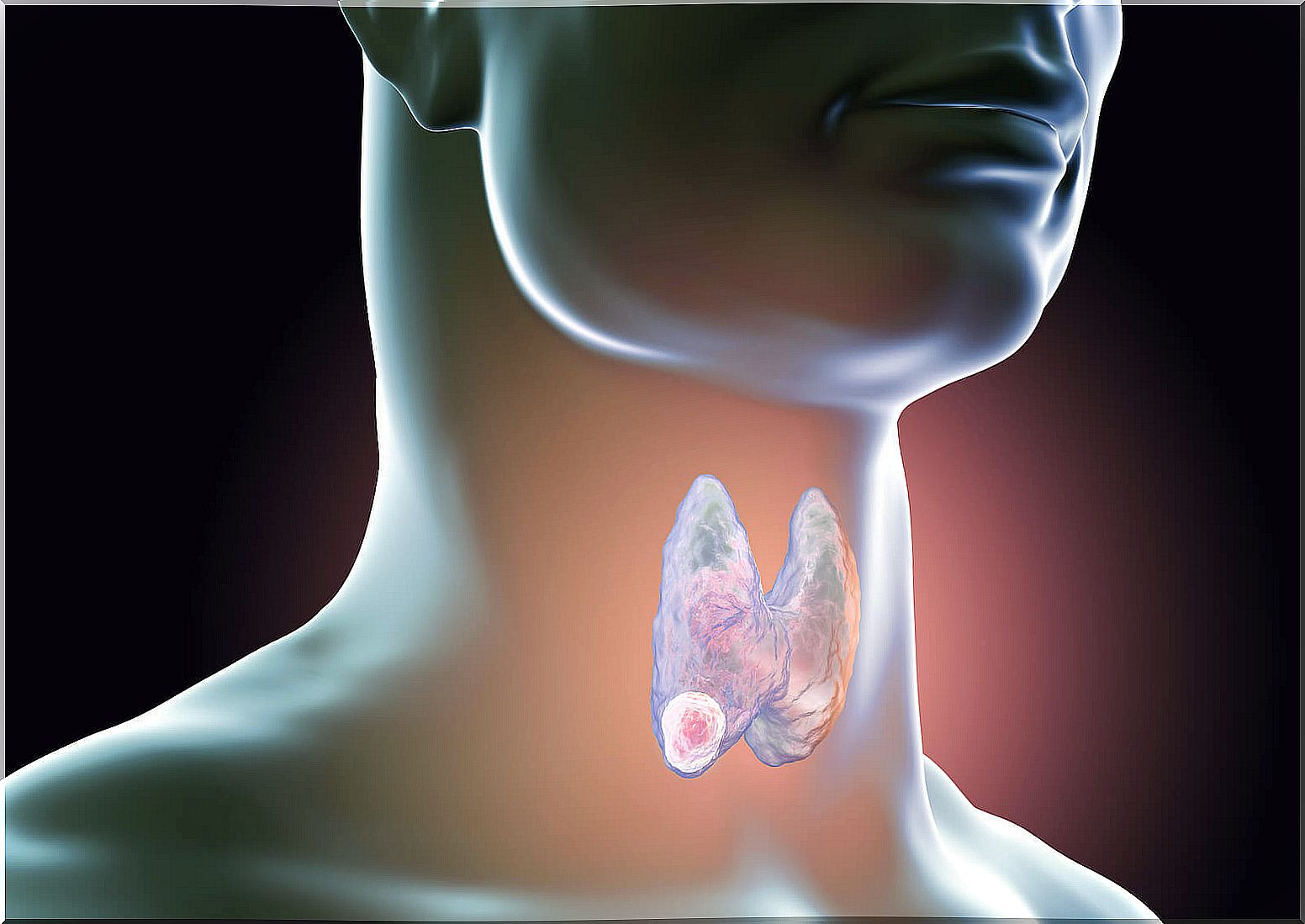
Types of thyroid biopsy
A thyroid biopsy can be done in different ways. In general, they are divided into two types: puncture and open. In the following sections we explain what each one consists of.
1. Puncture biopsy
A puncture biopsy is one that is performed with needles of different gauge. Within this group we find the fine needle aspiration biopsy. It is the most used. As explained by specialists from the Mayo Clinic, a thin, hollow needle is used to extract the cells.
It is usually combined with a simultaneous ultrasound to direct the needle to the specific point. This technique is performed in the hospital or in the office itself. It lasts about 10 minutes and does not require general anesthesia, as it is a minimally invasive test.
To perform it, the patient must lie on his back, with the neck extended. It is essential that you remain still and quiet during the process, as any movement can interfere with the direction of the needle.
A needle biopsy can also be done with a thick needle. It allows to extract samples the size of a grain of rice. It is important that samples are obtained from the different nodules in the gland.
Once the process is finished, the area is cleaned and a bandage is placed on the points where the needle was inserted. It is normal that afterwards there is a slight discomfort in the area.
2. Open biopsy
Thyroid biopsy can also be done by surgery. In these cases it is called an open biopsy . It consists of making a small cut in the neck and removing the nodule or taking a smaller sample to send it to the laboratory.
In some cases, a large part of the gland is removed. This technique is indicated when the needle biopsy has not given an accurate diagnosis.
General anesthesia is required for this surgery and must be carried out in the operating room. It is less used because it presents more risks. For example, it increases the chance of infection, bleeding, and healing problems.
Why is a thyroid biopsy performed?
A thyroid biopsy is done to determine the cause of a nodule (lump) that appears in the gland. Most are detected in advance through a physical examination. They may also have been seen by an ultrasound or a scan.
Thanks to this test, the cells that make up the nodule are observed. This allows to check if there is malignancy and if it is a cancer or not.
Thyroid biopsy is also used to study certain cases of goiter. Goiter is the enlargement of the thyroid.
How to prepare for this procedure
Before performing a thyroid biopsy, it is essential that the doctor know the patient’s medical history. You should know if you take any medication or if you have any other pathology. A previous examination is also necessary to locate the nodules.
The usual thing is that certain complementary tests are carried out before the biopsy. For example, a blood test and an ultrasound.
No specific preparation is required for needle biopsy. As it is an outpatient test and without general anesthesia, it is not necessary to do a previous fast.
If the thyroid biopsy is open, general anesthesia will be used. As it is a more complex intervention, specific indications will be given to the patient. In this case, you should not eat or drink before the procedure. In addition, it will be necessary to remain at rest during the following hours.
Possible results of a thyroid biopsy

The thyroid biopsy offers a lot of information about the state of the gland. When the sample is analyzed in the laboratory, an extensive report is made that describes different parameters.
First, the color, consistency, and overall appearance are explained. Then we proceed to describe the cells that compose it, both in number and morphology. In this way, as explained by the American Thyroid Association , the results of a thyroid biopsy can be the following:
- Benign – Most biopsies provide this result. They are nodules that are made up of differentiated cells, without atypia. A regular follow-up is usually carried out in the following months and it is not necessary to intervene.
- Suspicious of malignancy: these types of results mean that there are certain characteristics that guide towards a diagnosis of malignancy, but they are not conclusive.
- Malignancy: it is when cancer cells are observed in the sample. The most common thyroid cancer is papillary. Treatment is usually surgery.
- Atypia of undetermined significance: similar to the category of suspected malignancy . However, although worrisome traits are observed, there are also characteristics that orient towards something benign. Ideally, repeat the biopsy if in doubt.
- Non-diagnostic: it is one in which not enough cells have been obtained to establish an accurate diagnosis.
Biopsy is a fundamental test for cancer
What we must remember is that, at present, the thyroid biopsy is the basic test to be able to diagnose the cancer of the gland. In fact, it not only reveals the presence of malignancy, but also allows the specific type of tumor to be identified.
In this way, it makes it possible to establish an adequate treatment protocol depending on the pathology. In addition, it is a test that is usually performed on an outpatient basis and has a low risk of complications.