Treatment Of Hypothyroidism
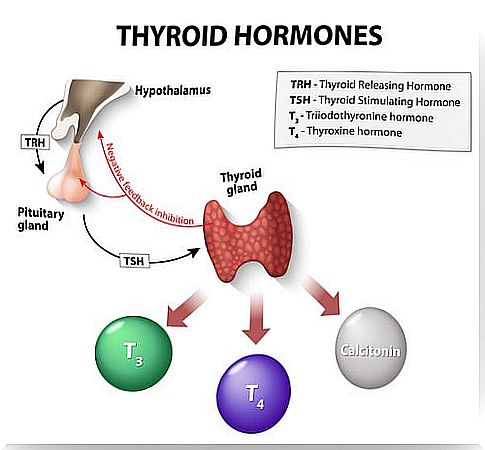
Treatment of hypothyroidism consists of restoring the level of thyroxine, a thyroid hormone also known as T4.
T4 is administered and not triiodothyronine (T3) because the former has a longer half-life. In addition, a part of the body is transformed into T3, so it is not necessary to replace the latter.
With few exceptions, treatment for hypothyroidism is lifelong. However, with the appropriate dose, hypothyroid patients do not have any limitation to their activities.
The drug used par excellence is levothyroxine, which should be prescribed with the lowest possible dose that is capable of restoring T4 levels.
Establishing the proper dosage
To establish the appropriate dose, the doctor will carry out an evaluation of the patient based on:
- The weight
- Age
- Medical history
After setting the dose, at six to eight weeks, the doctor will perform other tests to measure the blood levels of T4 and TSH. Thyrotropin or TSH is the thyroid stimulating hormone, it is produced in the pituitary gland to regulate the production of thyroid hormones.
If the test does not reflect physiological conditions, the patient’s drug dose will be changed until the results are adequate.
A well-treated hypothyroid patient is one who has a weight for height, T4 and TSH levels in normal ranges.
Considerations
There are some specific cases in which the dose adjustment has to be more specific:
- People over 60 : the dose for these people should be lower than in younger people. The adjustment should be gradual to prevent heart problems.
- Pregnancy : women who are pregnant will probably have to adjust their dose again.
- Babies, children and adolescents must undergo periodic examinations. The dose should be less than that of adults as it is based, in part, on the weight of the person.
- Adults and children who have had thyroid cancer. These patients must take levothyroxine to prevent the pituitary from producing TSH. Without it, the thyroid does not grow and the possibility of relapse into another cancer is reduced. They need to have medical tests more often to prevent heart and bone problems.
recommendations
A number of guidelines are recommended if you are being treated for hypothyroidism, including:
- If you decide to change the brand of medicine you are using, you must inform your doctor to avoid any complications.
- It is advisable to take the medication on an empty stomach. Diet can interfere with the absorption of the drug, especially diets rich in soy or fiber.
- Even if symptoms improve, you should not abandon treatment without first consulting your doctor.
- Caution if you take food supplements or medicines that bind bile acids. It is recommended to wait approximately 4 hours before administering the treatment.
- Maintain a balanced diet, patients with hypothyroidism tend to gain weight, so a diet low in fat and rich in fruits and vegetables is recommended.
You should also be aware of these symptoms if you are under thyroid hormone replacement therapy and discuss them with your doctor:
- Rapid weight loss
- Sweating
- Restlessness or tremors
- Palpitations
These symptoms are typical of an over-activity of thioridal hormones. Hypertoridism can occur if we have a higher dose than required.
Other alternatives in the treatment of hypothyroidism
There are some patients for whom two other treatment options are considered:
- T3 and T4 tablets. These pills can cause adverse effects such as anxiety. Despite this, some patients say they are better with this prescription than with T4 alone.









